Investigation and determination of Activity from Trans plutonium element in sediment of Caspian Sea
By:Iraj Bayat, Ph.D. Faculty Member, Retired from Iran Atomic Energy Organization Seyed Hossein Omidiani, Ph.D., Associate member of Physics Association and Solar Energy Association of Iran
Abstract:
To study the behavior in environment and to measure plutonium in the sediment of sea, a quick sensitive analytical method is required, can be applied to all sample materials found in the environment. Of the method, published only few reach the detection limits required for the application to all material and with those methods expenditure in time is either to high or applicability to all materials found in the environment is not ensured.
A boiling out method using HNo¬3¬ was found to be successful for a soil contaminated with fall out plutonium.
Abstract:
To study the behavior in environment and to measure plutonium in the sediment of sea, a quick sensitive analytical method is required, can be applied to all sample materials found in the environment. Of the method, published only few reach the detection limits required for the application to all material and with those methods expenditure in time is either to high or applicability to all materials found in the environment is not ensured.
A boiling out method using HNo3 was found to be successful for a soil contaminated with fall out plutonium.
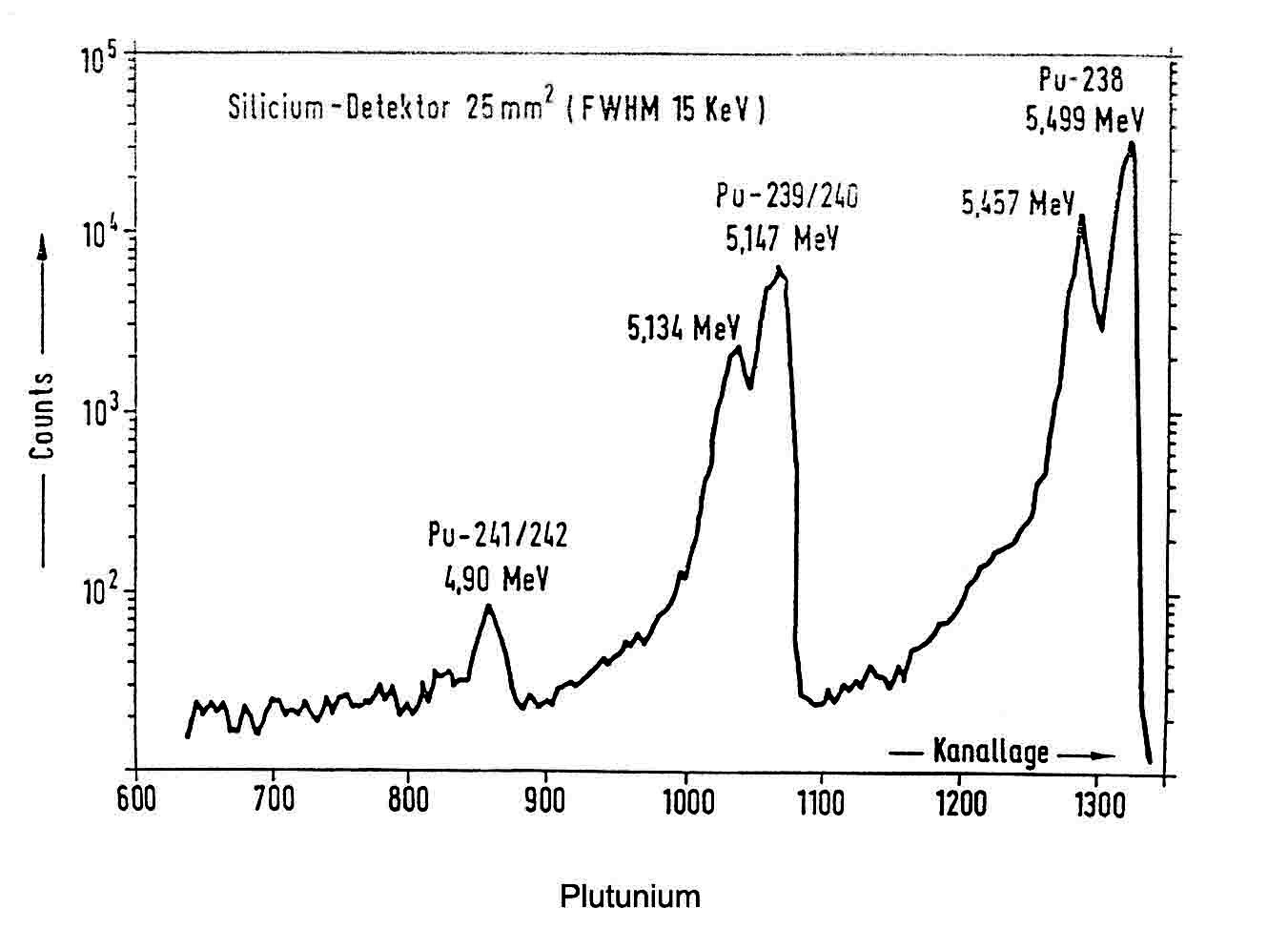
Use of HNo3 for boiling out plutonium from sediment samples having the properties of Iron exchange or with a content of plutonium coprecipitating substances has show that although the chemical yield is slighty roduce. The plutonium contamination can be exactly determined from 500 ml of leaching solution the portion of dissolved matrix element is seperated practically in quntitative term by extraction with trioctyl-phsphonic oxide (TOPO). Back extraction tabes place with a scorbic acid/Hcl. The methods of radiochemical cleaning for separation of disturbing a-emiters and residues of the matrix consist of LaF3 coprecipitation and Ionig exchang. Amng three electroplatation techniques Investigation of preparing a-spectrometry atechniques based (NH4)2 C2o4 was found to be optimum.
An analytical method was worked out for plutonium, which can be applied to all materials found in environment.
The sample size is 100gr but it migt also bemuch greater. The average chemical yield is 70 and 80%. Thedetection limit for sample 0/1 fci/g. The analytical procedure was applied to a large number of environmental samples and the results analysis are indicated with standard.
Kay Word: Plutonium, Radioactivity, Alpha spectrum, Environment, Sediment.
Reference:
1- Management of separated Plutonium Th Royal Society February1998.
2- Annual Reports on Radioactive Discharges and Monitoring Environment, BNFL Risly, Uk1977-1995.
3- Aguatic Environment Monitoring Reporte Minister Agriculture Fisheries and Food Lowest off, Uk 1971-1989.
4- Crusius, John, and R. F. Anderson. 1995 Evaluating the mobility of 137 Cs, 239+240 Pu, and 210 Pb form their distributions in laminated lake sediments: Journal of Paleolimnology13: 119-141.
5- KFK 4516 March1989, Plutonium Redaktion: W. Koeizer.
6- N. A. Talvite Electrodeposition of Actinides for Alpha spectrometry Determination Analchem Vol 44 No.2, 280 (February1977)
7- I. K. Kressin Electrodeposition of plutonium and Americium for High Resolution a-Spectrometriy Analytical chemistry; Vol 49, No, 6: 842 (May 1977).
8- H. Schifer decker Bestimmung von Rudionuckleliden in Biological Material KFK 810 Kernforschungs-zentram Korlsruhe (Nov 1980)
9- C. Keller The chemistry of the Transurainium. Elements Verlag chemie, Weinheim (1971).
10- Marsh, S. P. 1992b Analytical results for stream sediment and soil samples from the Commonwealth of puerto Rico, Isla de Culebra, and Isla de Vieques: U. S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 92-353B Data on a 5.25 inch diskette.
11- Puerto Rico Environmental Quality Board 1990 Puerto Rico water-quality standards regulation, as amended. 100p.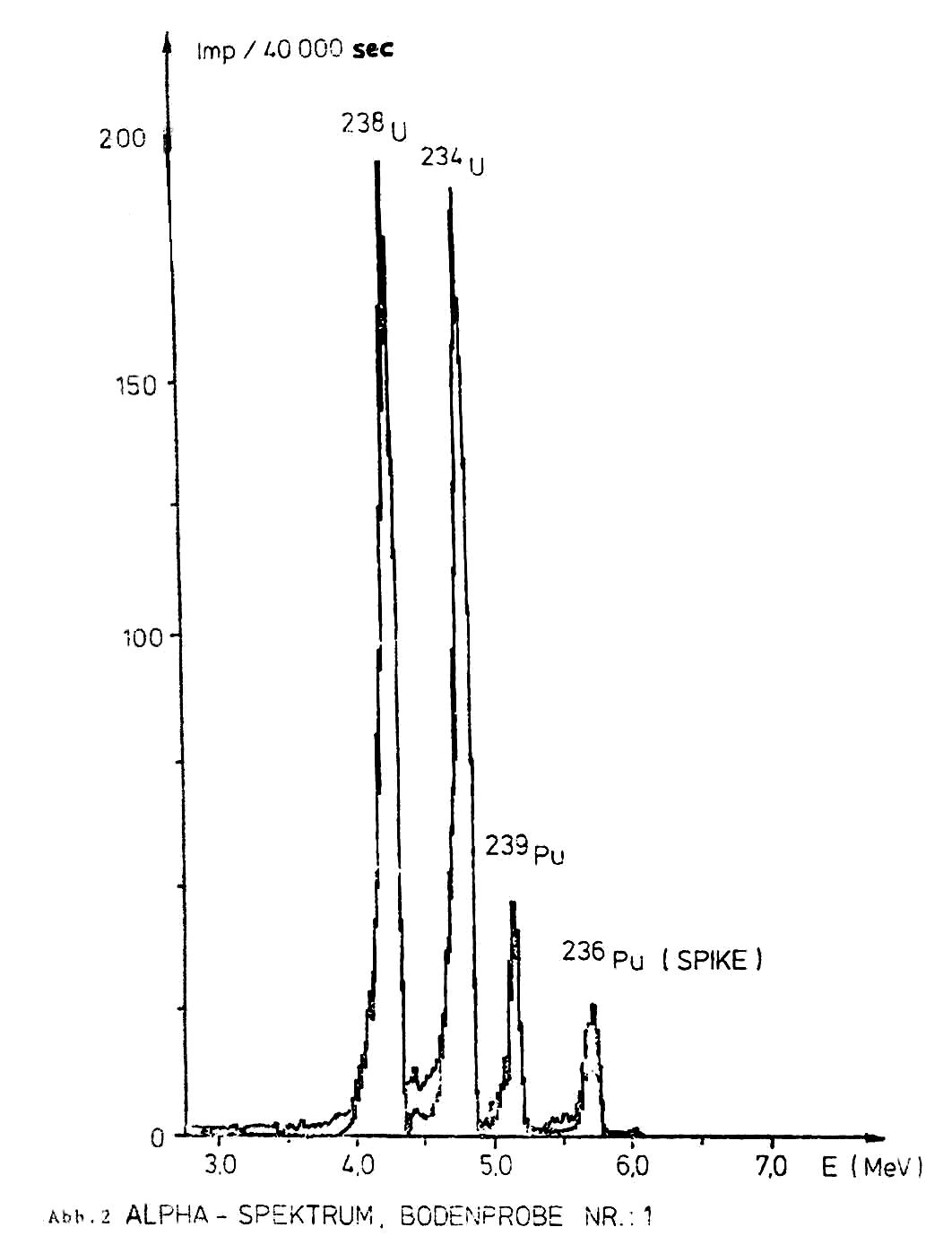
 گزیده ای از تازه های نجومی و بخش هایی از مقالات، تالیفات و سخنرانی های دکتر سید حسین امیدیانی:
گزیده ای از تازه های نجومی و بخش هایی از مقالات، تالیفات و سخنرانی های دکتر سید حسین امیدیانی: